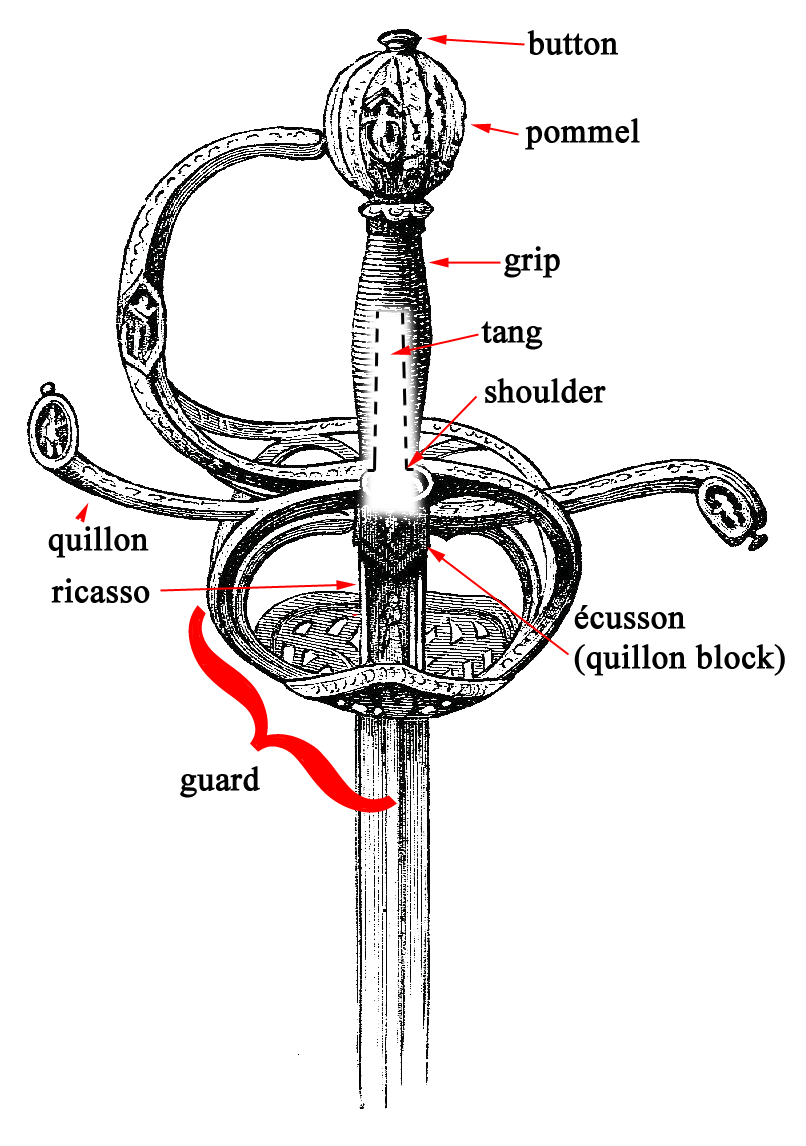
There is no such thing as a generic or universal sword, thus no single drawing can encapsulate all the possible parts and various names for them. The diagram I made here is based off a Renaissance-style rapier, which is what many of us traditionally keep in our stock and use for stage combat. Interestingly, swords in all time-periods and cultures share at least three basic parts: the blade, the pommel, and the grip.
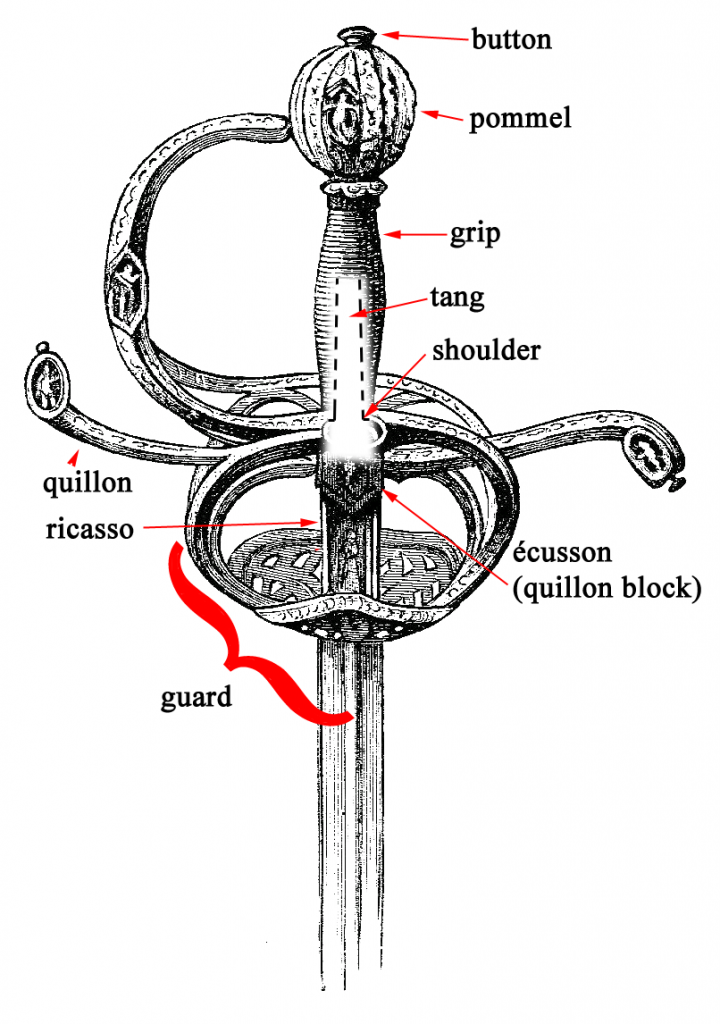
Button – Also known as a pommel nut, pommel bolt, capstan rivet, or tang nut. In some swords, the button is screwed on to the end of the tang to hold the grip on.
Pommel – The counter-weight at the end of the grip.
Grip – Handle
Tang – The hidden part of the blade which the grip is mounted to.
Shoulder – The corner portion where the tang and the blade meet.
Guard – A blanket term for all the parts that protect the hand.
Quillon – Extended portions of the guard.
Écusson – or quillon block. The metal center where the quillons meet and all parts of the guard attach to.
Ricasso – Unsharpened portion of the blade which extends from the grip to the end of the guard.