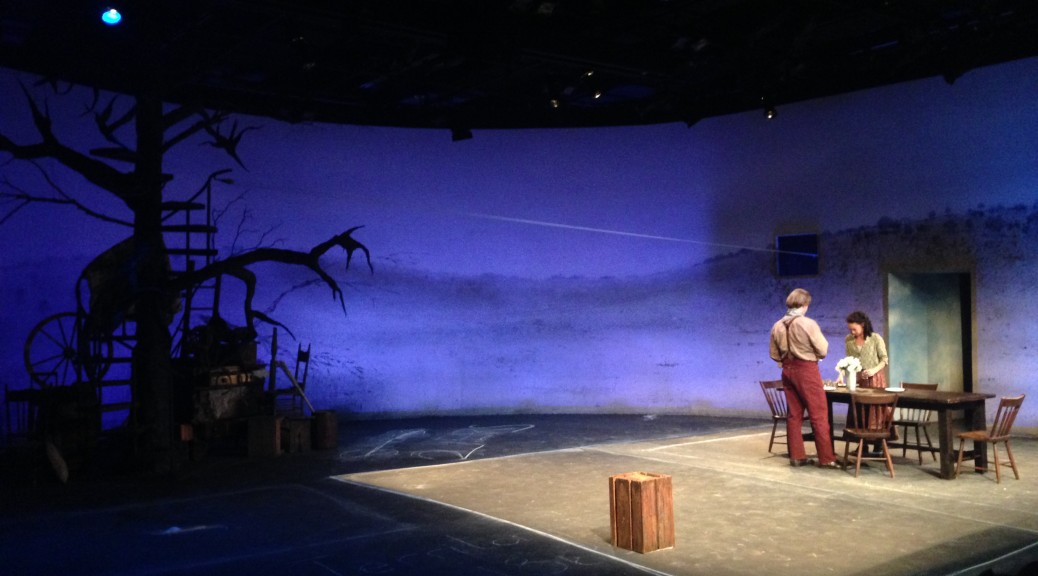
Last spring, Triad Stage did a production of Abundance, one of the lesser-performed plays by Beth Henley. It was directed by Preston Lane, with scenic design by Robin Vest. One of the main furniture pieces was a giant farmhouse table. I decided to build it because finding a farmhouse table this size would blow the budget, and they are usually pretty hefty.
It needed to be super sturdy but fairly lightweight, because they jumped up and down off of it, flipped it onto its side, and dragged it around on stage. To cut down on the weight, only the boards around the perimeter of the top were the full thickness; the ones on the inside were thinner, with a bit of hidden framing to sturdy them up.

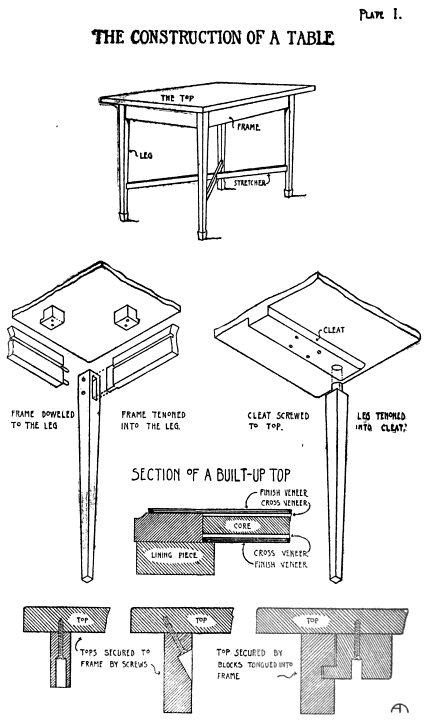
The breadboard ends allowed me to hide the different thicknesses of wood used for the top. I positioned the legs so they would straddle the joint where the breadboard was attached so it would not snap off if the actors ever stepped on the very edge.
I also made the legs hollow. They were made from four pieces of wood with mitered edges glued together. To save time, I glued up four long pieces of wood, and when dry, cut it into the four legs.

The research images for the table led me to a website called “Ana White”, which also had plans for the table the designer liked. I’ve since come across several woodworking forums which resent White’s style of furniture, since it seems to be flooding the market with this kind of shabby chic table that won’t hold up to seasonal changes. Ah well, the look was right, and it was easy to slap together.

I experimented with some new (for me) finishing techniques to get a really aged, rustic appearance. The first step was scorching the entire surface with a propane torch and rubbing the charred wood away with steel wool. It took forever; I wonder if an oxy-acetylene torch would have been faster, or if it would have just started an unstoppable fire.

After that, I rubbed an oxidizing solution over the whole thing. You can find instructions on various websites; basically, you let a piece of steel wool dissolve in vinegar for a few days. Apply it to the wood with a paintbrush and it starts to darken and grey the wood over the next few hours. Once it was all done, I rubbed a coat of paste finishing wax onto the whole thing.

It ended up being a great table for the show. I could actually carry it around myself, though for the show, it was always two actors moving it. It only started loosening up during the last show, after weeks of being tossed up on its side, which placed a lot of stress on its legs.