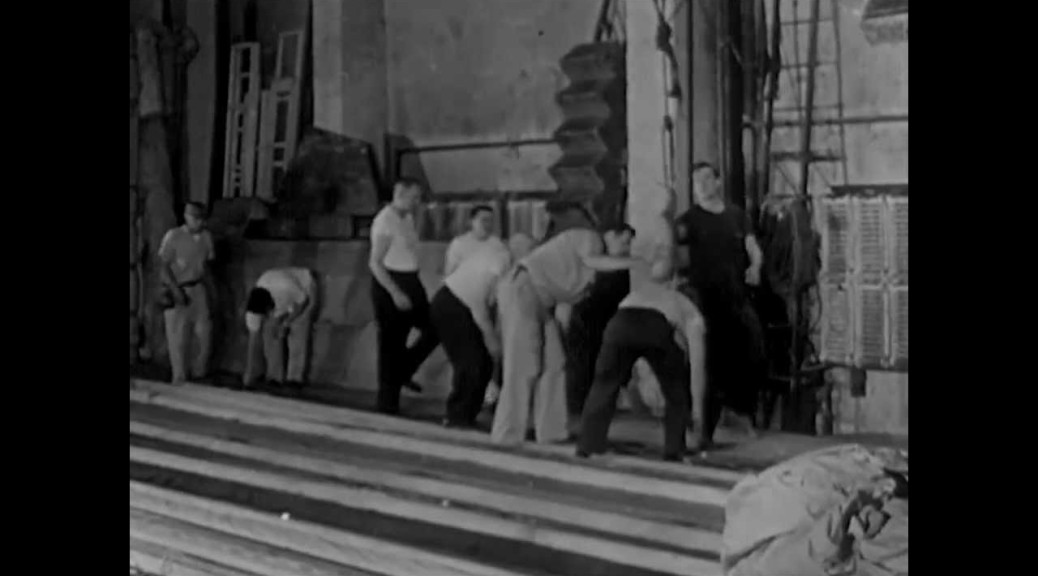
This has already been making the rounds, but it’s too good not to share. The Prelinger Archives has a short film from the 1960s about theatre stagehands at work. Part of the “Americans at Work” series presented by the AFL-CIO, this ten minute video shows how much things have changed in the past fifty years (and, more interestingly, how much has stayed the same).
Tag Archives: stagehand
TGI Links
This is from a few years ago, but it should provide a lengthy diversion: The New York Stagehand Glossary. It has a lot of terms which should be familiar to many of us, along with many I have heard for the first time (which is understandable, because I only did a bit of work as a stagehand while living in New York City).
Back in the old days, inventors who applied for a patent also had to submit a model of their invention. These models ranged from simple craft attempts to miniature marvels of engineering. The Rothschild Petersen Patent Model Museum houses one of the largest collections of these models, most dating from the 18th and 19th century. You can also view this set of photographs showing more of the models and exhibits.

Most props people are familiar with Mortite and floral putty for temporarily securing props to shelves, trays and tables. Sometimes, though, you want something a little stronger; you may even need something clear, such as when you need to secure crystal to a glass surface. Quakehold! has a whole bunch of products intended for securing your collectibles and valuables to shelves at home in case of earthquakes. Materials such as Museum Wax, Museum Putty and Museum Gel should keep your props from tipping or falling, and can be cleanly removed when the show is finished.
I like this tutorial for repairing broken plastic items with solvent welding with one caveat: you need to wear the proper gloves and skin protection as well as provide adequate ventilation and respiratory protection.
At the Props Summit a few weeks ago, they mentioned InFlow, an inventory management software program which can be used to catalog and track inventory. It was suggested that it might be useful for maintaining a photographic database of your stock. I haven’t used it, but the website offers a free download (you are limited to 100 items in your database) in case anyone was interested in trying it out.
Backstage Views from 1900.
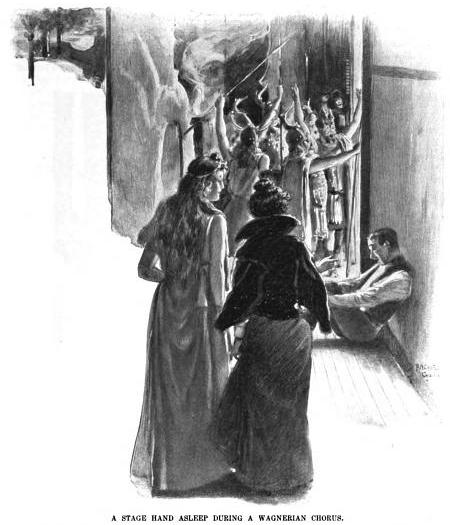
I found the following images in a copy of “The Century Illustrated Monthly Magazine” from 1900. They appeared in an article about performing Wagner’s Ring Cycle. I love how they give a glimpse of what backstage life was like over a hundred years ago. In most respects, it is very much unchanged from the present form.
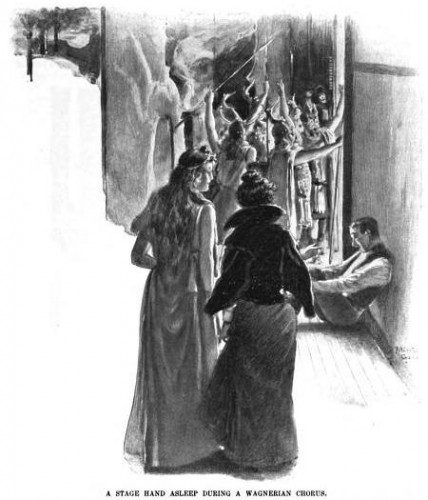

Though asleep, the stage hand above is “better dressed” than the typical stage hand today. Than again, most stage hands need to wear all black clothes, and the fabrics today stand up to much more wear and tear and are easier to clean than the suits and trousers of 1900.

I love the looks of these chorus members as they wait for their moment on stage. What is also interesting is the flat in the background, which is constructed in exactly the same way that modern flats are.

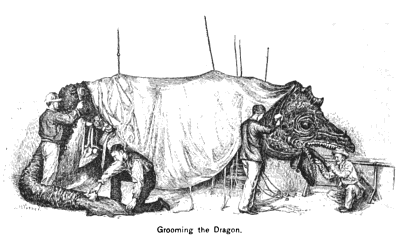
This moving dragon shows a low-tech but reliable solution that is still utilized in all but the highest-budget performances today.

The wagons which carry these boys would not look out of place in a modern opera production. I find it interesting again how the stage hand is dressed; it is not just that he is wearing a vest and tie, but that his shirt appears to be white rather than the dark colors we usually wear back stage.

Finally, this illustration goes to show you that back stage areas have always been cramped.
Images originally appeared in “The Century Illustrated Monthly Magazine, Volume 59, Richard Watson Gilder, The Century Co, 1900.
How to Build a Dragon
I previously shared an article from 1888 about a giant dragon named Fafner used in the Metropolitan Opera’s performance of Siegfried. It had a papier-mâché head, a canvas hide and curled leather scales. It could move its mouth, close its eyelids and issue forth steam from its lungs. So who created such an impressive piece of stage property?
It would appear a man named William “Old Bill” E. De Verna constructed it. He was born in Bay Ridge, Brooklyn, NY, in 1834, and died in the same neighborhood in 1897. He had achieved enough prominence in the theatrical world to have an obituary published in The New York Times, with his occupation listed as “maker of theatrical properties.” According to the obituary
He built a large factory called in Bay Ridge the “dragon” factory, where he manufactured scenic accessories. When the Metropolitan Opera House was built he was engaged to supply all the properties used in the German opera. The big dragon of “Siegfried” was considered one of the most perfect examples of the property maker’s art.
A second dragon was built for the Met around 1911. In 1937, the Metropolitan Opera made a few improvements to this second iteration of Fafner. A “New Yorker” article describes how they replaced his metal scales with a painted canvas hide to cut down on his weight.
Like the original, the 1937 dragon also had a papier-mâché brow. It could “prance around”, open and close its jaws and spread its fins. It was operated by two stagehands, Charley Walters and Paddy Downey, who had been playing Fafner since around 1922. They were not chosen for any specific reason; Phil Crispano, the head property man, “just told them to get in there one day.” The smoke from the dragon’s nostrils was at one time supplied by live steampipes, but has since been replaced with a vapor made from ammonia, muriatic acid and rose water (to improve the smell).
Interestingly, the 1888 article describes the scene with the dragon as lasting forty minutes, while the 1937 articles says it was over in just fifteen.
A new dragon was commissioned in 1948 to replace the “the ancient bundle of canvas and rubber hose the Met has seen fit to fob off for thirty-seven years as Fafner”. This one was built by Messmore and Damon, a company headquartered on West Twenty-Seventh Street in Manhattan. Messmore and Damon were known for the full-scale mechanical dinosaurs they debuted at the 1933 Chicago World’s Fair.
According to another article in the “New Yorker”, this new dragon took advantage of the company’s prowess in mechanical engineering, as well as the new breakthroughs in materials available to prop makers. The jaw could move, the tongue could flick in all directions and the eyes could roll in their sockets. The whole cave was moved downstage so he could be seen better; traditionally, the dragon appeared far upstage, probably to conceal the limitations of dragon construction at the time. The paw of this Fafner actually dangled into the orchestra pit. He was also split into two pieces; his head came out of the wings downstage, while his tail appeared from the wings upstage to make it appear that a much larger dragon was present just offstage.
The 1948 Fafner’s teeth were constructed of solid maple, his tail was foam rubber and his claws had rubber tips. Real steam was used for his nostrils once again—the chemical smoke caused the singers to cough—though now it was provided by a portable steam generator.
And the cost for this modern marvel? A whopping two thousand dollars. Okay, so that’s actually just over $19,000 today, but still, being able to buy a custom working dragon for less than the price of a new car is pretty spectacular.
Friday Props Links Roundup
The Guardian has a nice little article on How to Make a Haunted House. It details how the set dresser, prop master and other members of the art department use locations, architecture and props to create the mood of the upcoming ghost film, The Woman in Black. They purchased and borrowed tons (or “tonnes”, as this is a British film) of Victorian-era objects and paraphernalia to dress the sets.
Have you heard of the new show Prop Freaks? Because it’s a TV show about people who make and collect props. Well, it’s a show in development; you can watch short clips on the website until it finds an audience. But it looks pretty cool, and I can’t wait to see more.
Here is an interview with Russell Bobbitt on how he uses 3D printing technology to create many of his props. Russell Bobbitt is the film prop master who has made some fairly recognizable props, such as the glowing chest piece from Iron Man 2, or the wristband laser gun from Cowboys and Aliens.
Here is an interesting video on using a vacuum former to make masks. There’s a few things that make this especially intriguing: his rig is portable so he is able to take it to an event where other people can vacuum form their own masks, and he uses a bicycle pump to draw out the air rather than a vacuum cleaner. Also, the music playing in the background is a Nintendo beat version of MOP’s “Ante Up” with computers rapping (done by an artist named “Danny Drive Thru”), so that alone makes this worth watching.
While not prop-related, this last link is pretty fun. Watch this time-lapse video of stagehands from IATSE local 33 set up the orchestra pit at the Walt Disney Concert Hall. It’s a pretty ambitious sounding project too; over 1,000 musicians will perform.


