First, I wanted to mention that I have redone and updated my online portfolio; it was in desperate need of an overhaul, especially now that I am freelancing again. I went with a free site at CarbonMade.com, because the thought of designing and coding yet another portfolio site was making me tired just thinking about it. I’ve seen some other prop makers who use that site to show their work, and so far, it seems to be working well. Let me know what you think!
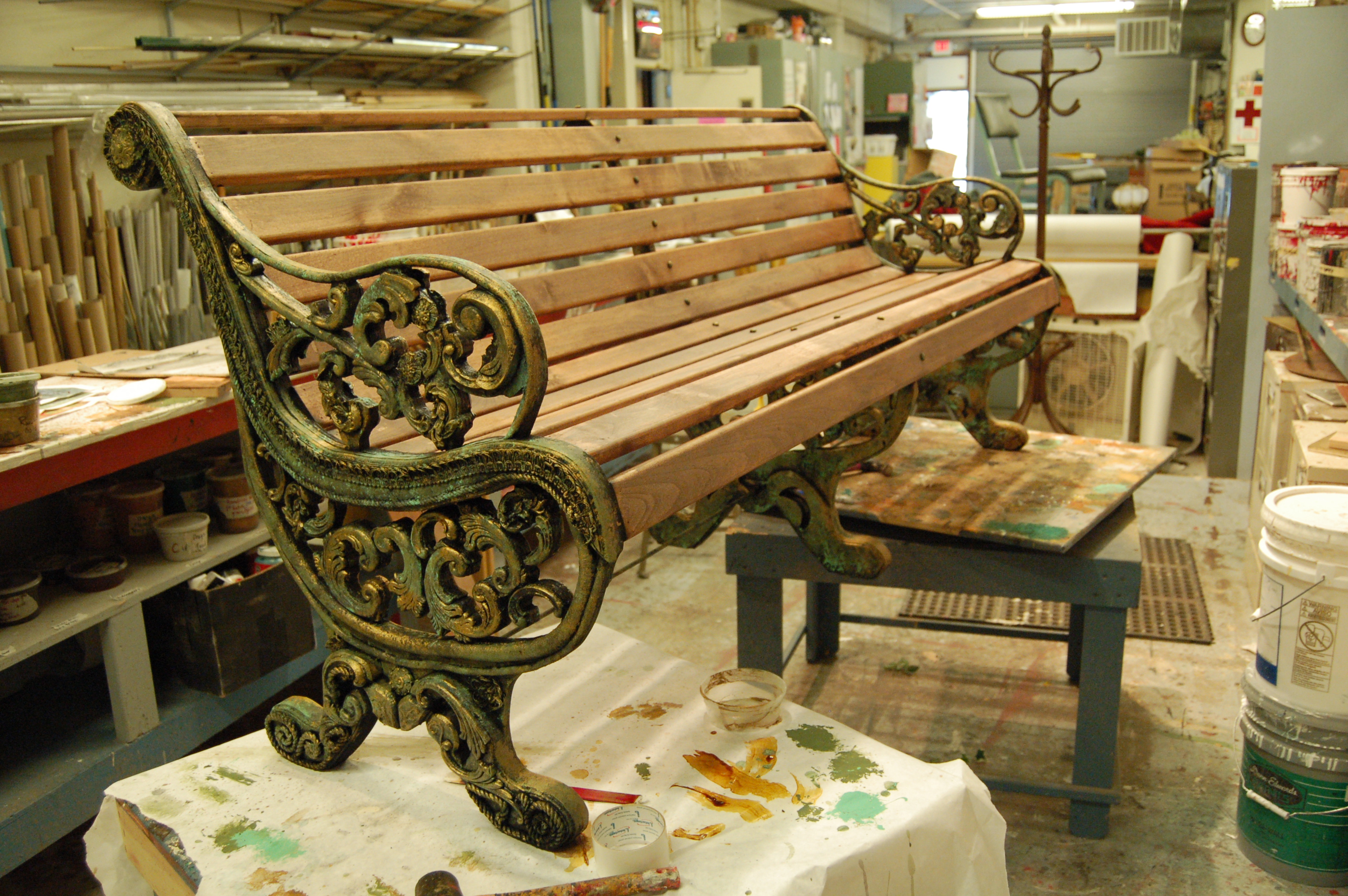
Now then, let’s take a look at a bench I made back in 2006 at the Santa Fe Opera. I basically had to build the whole thing from scratch in less than a week, so it’s a bit rough.

They wanted a cast iron park bench. The only real requirements were the size, so I had to find my own research image. I showed the above photograph to Randy Lutz, the prop master, and he agreed it was a good bench to duplicate.

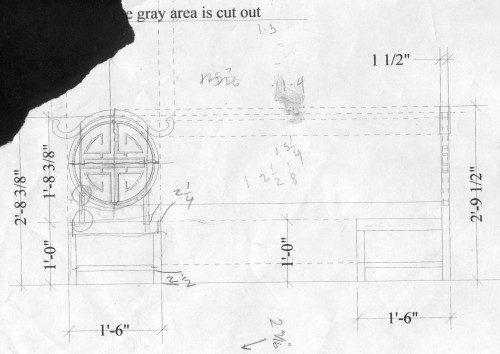
I drew a full-scale layout of the side on a piece of paper and spray-glued it to a sheet of plywood. You’ll notice the decorative parts do not match the photograph exactly. What I decided to do was pull some decorative resin castings and carved wood pieces from stock—the opera has quite a good collection of these. I then arranged them to match the research as closely as possible. I traced them and cut away the extra plywood. You’ll see in a bit when I start gluing them on, it’ll all make sense.

I cut out and added some support runners on the insides of the two ends and began to attach the slats which would make up the back and the seat. It needed some extra support, so I ran a rod along the bottom; you can see it in the next photograph.

Now I began attaching the decorative resin bits. I also used some Ethafoam rod cut in half to make some curved half-round molding. I found a strip of upholstery fringe which added more texture.

Here’s a closeup showing some of the resin bits and Ethafoam, as well as some rosettes and even bits of yarn. If you look really close, you can even make out a bit of hot glue design work; though it’s practically invisible here, once the paint goes on, it will add just that extra little bit of texture that will make the whole thing seem like a single piece of cast iron from the audience.

The paint job is what really helped marry all the different materials together and bring the whole thing to life. The painter of this bench worked as one of the other props carpenters for the beginning of the summer, so none of us knew how good he was at scenic art until he did this bench.

So here it is, ready to go on stage. I even added some round bolt heads running down the middle so it looked like the slats were bolted to the legs. Overall, it was a fun piece for the short time frame I had to build it in.